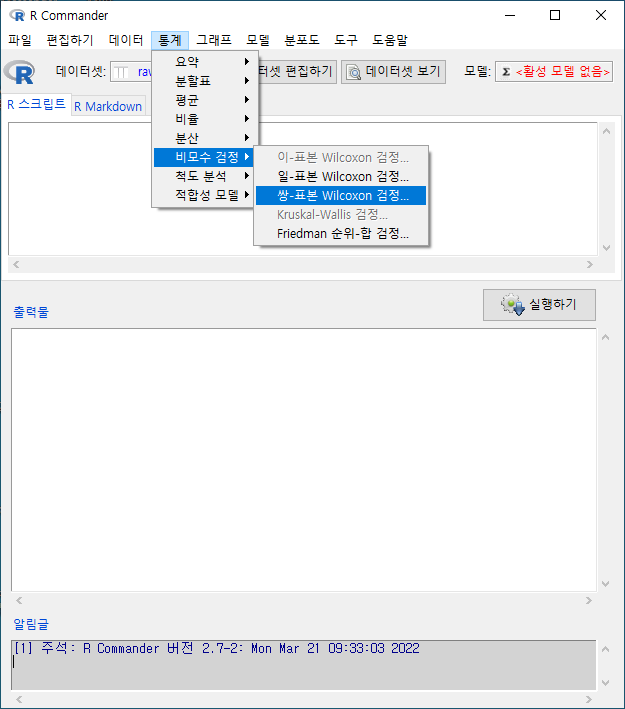
통계 > 비모수 검정 > 쌍-표본 Wilcoxon test...
Statistics > Nonparametric tests > Paired-samples Wilcoxon test...
depression 이라는 이름의 데이터셋을 만들자. first, second, change 라는 세개의 변수를 갖는다고 하자. change 변수는 second와 first의 차이를 사례 값으로 갖는다고 하자. 아래와 같을 것이다.
first <- c(1.83, 0.50, 1.62, 2.48, 1.68, 1.88, 1.55, 3.06, 1.30)
second <- c(0.878, 0.647, 0.598, 2.05, 1.06, 1.29, 1.06, 3.14, 1.29)
change <- second - first # compute new variable 참조할 것
depression <- data.frame(cbind(first, second, change)) # 세개의 vector를 묶어 데이터프레임으로 전환2. Compute new variable...
새로운 변수 계산하기... Data > Manage variables in active data set > Compute new variable... 활성 데이터셋에 있는 변수들을 활용하여 새로운 변수를 생성하는 많은 방법이 있다. 은 일반적으로 수치형 사..
rcmdr.kr
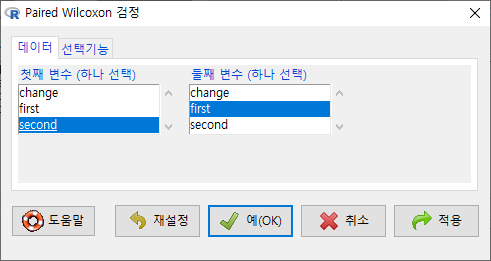
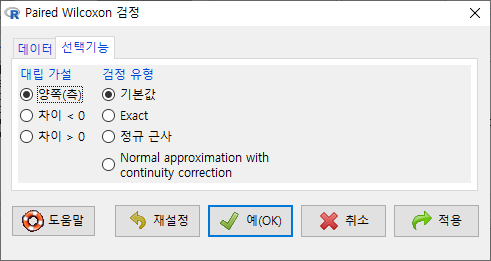
<선택기능> 창에 있는 기본 선택 사양을 그대로 사용해보자. <대립 가설>에서 '양쪽(측)'이 선택되어 있다. depression 데이터셋의 second 변수와 first 변수 사이에 순위 차이가 있는가를 살펴보는 것이라 할 수 있다.
with(depression, median(second - first, na.rm=TRUE)) # median difference
with(depression, wilcox.test(second, first, alternative='two.sided',
paired=TRUE)) # 양측 검정
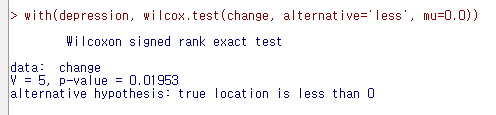
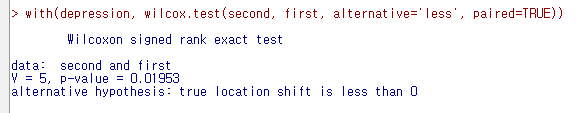
with(depression, wilcox.test(second, first, alternative='less', paired=TRUE))
# 단측 검정 ( 차이 < 0 )
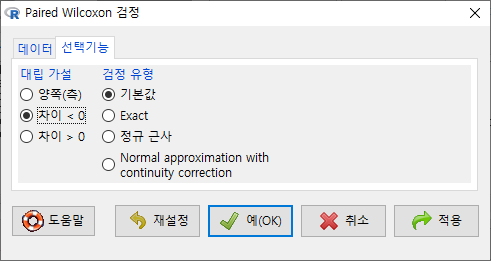
<선택 기능> 창에서 <대립 가설>에 '차이 < 0'를 선택하자. second 변수의 사례 값이 first 변수의 사례 값보다 작아졌는지를 점검하는 것이다. (depression이 작아졌다는 것은 개선되었다는 의미로 해석될 수도 있다.)
'Statistics > Nonparametric tests' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2. Single-sample Wilcoxon test... (0) | 2022.03.21 |
|---|---|
| 1. Two-sample Wilcoxon test... (0) | 2022.03.21 |
| 5. Friedman rank-sum test... (0) | 2022.03.20 |
| 4. Kruskal-Wallis test... (0) | 2022.03.09 |